Affiliate Disclosure: As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.
When you have multiple devices and people within the home looking to access the Internet at the same time, each one of them will be consuming part of the bandwidth you have available. Depending on how much you have, you may soon find yourself experiencing poor video streaming or suffer a defeat in your favorite online game due to lag as a result of a particular device consuming a large proportion of the bandwidth.
Bandwidth can be allocated on a home network. Quality of Service can be used to allocate different services, or even individual devices, priority of the bandwidth that is available to you.
You may pay your Internet Service Provider for a set amount of bandwidth, however, it is up to you to manage how this bandwidth gets allocated. This can be easier said than done, particularly in a large home with a growing number of devices. It can be hard to manage what is connecting to the Internet and at what time.
How to Identify Devices Using Lots of Bandwidth
Windows PCs and Laptops
If you, or others within your home, begin to experience performance issues, or perhaps you are limited by the amount of data you can use by your ISP, it can be useful to monitor the bandwidth usage of the devices on your home network and identify who, or what device, is consuming a lot of your bandwidth.
If you have a suspicion that a particular Windows PC or laptop is hogging your bandwidth, you are probably best installing a piece of network usage monitoring software on to the suspect device first.
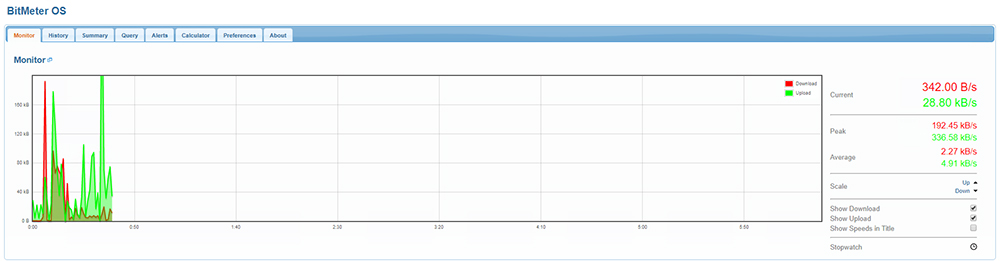
Two options to consider are NetWorx, which is a free application, or BitMeter OS, which is also free and open-source.
Both will be able to monitor bandwidth usage over time for the PC or laptop they are installed on.
They offer useful outputs of data in the form of charts and tables, making it easy to review.
Another convenient feature is the ability to set a quota for the device and be able to receive an alert when the quota is being approached or exceeded.

What About Other Devices?
Where these free applications fall down is that they can only be used on devices using the Windows operating system.
Most homes will have many different devices connected to the network, including smartphones, smart TVs, video game consoles and tablets; all in addition to the Windows-based devices.
Ideally, you would be able to monitor the entire network’s bandwidth from a single place, rather than having to install a piece of tracking software on each and every device.
In this case, the network traffic needs to be monitored from the router itself, or a device placed between the devices and the Internet connection itself.
Unfortunately, most routers will not offer the feature of being able to track bandwidth usage by individual device, but it is definitely worth checking first in case your router does.
If you are serious about finding the bandwidth hog, you could go as far as replacing your current router with one that does support this tracking feature.
A quick reference to the product manual, or perhaps even an email to the manufacturer, should soon tell you if this feature is available.
If you’re not keen on replacing the router, an alternative option is to flash your current router with aftermarket firmware, again assuming your router has this capability.
One choice for a popular piece of aftermarket firmware is DD-WRT as it supports many different brands and models of routers. The downside is that it will only show total bandwidth consumption.
Add-ons like DDWRT-BWMON are available, though, which allows you to identify usage on an individual device level.
If you don’t feel like these solutions are appropriate and are feeling bold, you could always build your own router.
If you have use of a virtual machine or even just a spare PC that is just lying around gathering dust, you could repurpose it and install an operating system that supports many network functions, including bandwidth monitoring, traffic routing, firewalls, and web filtering.
Two good options are Untangle and Sophos UTM.
How to Use Quality of Service to Allocate Bandwidth
Although many routers do not support built-in bandwidth monitoring tools, thankfully most do have a Quality of Service (QoS) feature, although it is not typically enabled by default.
QoS is designed to regulate bandwidth usage on the network to ensure good performance whilst also giving different types of traffic priority both on the network and with access to the Internet.
The type of traffic that gets priority are those that are particularly sensitive and where any developing lag is easily noticeable. These include:
- Online gaming
- Streaming video
- VoIP (Voice over IP) calls
Some examples of traffic types that aren’t sensitive to lag and therefore do not get priority with QoS enabled are:
- General web browsing
- Software updates
- Downloads
The extent to how you can manage QoS will vary depending on the manufacturer and model of your router, however, most will allow you to specify which devices should receive priority of the bandwidth simply by selecting the MAC address or the IP address of the device.
The type of service can also be tagged for it to be prioritized.
Some routers will come with a QoS configuration which the manufacturer has set to cater for the majority of users, however, these can be changed to best suit you and your network.
To access QoS (should it be available), simply login to your router and browse to the QoS settings.
If it is unclear as to where these settings are found, a quick review of your router’s documentation should point you in the right direction, or tell you that the feature is not supported.
The default settings will likely give priority to the more commonly used services.
If not, I would first recommend changing QoS so it prioritizes traffic based on the service type, if possible.
First, see if this helps resolve any performance issues you are facing. If not, you can always resort to selecting the individual devices you wish to be given priority.
Conclusion
If you are experiencing performance issues on particular devices, such as lag when online gaming or buffering when trying to stream an online video, there may be a device connected to your network that is hogging the bandwidth.
The first step is to identify said device; there are a few ways you can do this:
- NetWorx or BitMeter OS to monitor bandwidth usage on individual Windows PCs or laptops
- Purchase a router with monitoring built-in
- Flash an existing router with firmware that supports monitoring. Examples include DD-WRT and the DDWRT-BWMON add-on
- Repurpose an old PC or configure a virtual machine to use as a router. Untangle and Sophos UTM are operating systems that support many different network functions, including bandwidth monitoring
It is possible to allocate bandwidth on a home network through the use of Quality of Service. This is a useful way of being able to select the type of service or individuals devices, that should be given priority of the available bandwidth.
QoS is managed through your router, and thankfully, most will support this useful feature.
My recommendation would be to first select the type of traffic or service you wish to prioritize. If this doesn’t solve your problem, you can always select the MAC address or IP address of the devices you wish to be given priority of the bandwidth.
Just remember, QoS may not necessarily be the answer to all of your problems. If you have a particular slow Internet connection, QoS may not help a great deal.
